The Role of Membrane Bioreactor in Achieving Higher Effluent Quality Standards
The Role of Membrane Bioreactor in Achieving Higher Effluent Quality Standards
Blog Article
How Membrane Layer Bioreactors Are Changing Water Purification Equipments
The emergence of membrane bioreactors (MBRs) represents a considerable advancement in the area of water filtration, merging organic therapy procedures with sophisticated membrane layer purification modern technologies. As global water deficiency intensifies, the duty of MBRs in helping with potable water reuse and sustainable water management comes to be progressively essential.
Summary of Membrane Layer Bioreactors
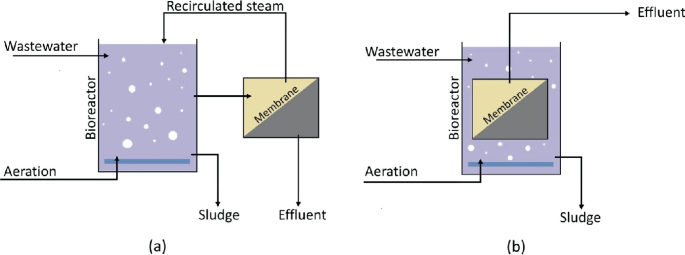
Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) stand for a substantial improvement in water filtration technology, as they combine organic treatment processes with membrane layer purification. This integration boosts the performance of wastewater treatment by making use of microbes to degrade natural pollutants while at the same time utilizing semi-permeable membrane layers to different cured water from put on hold solids and microorganisms.
The MBR system generally contains a biological activator where the microbial population metabolizes pollutants, complied with by a membrane filtration system that preserves biomass and allows just clean water to travel through. This double capability leads to higher effluent high quality compared to conventional treatment techniques. MBRs can be operated in both batch and continuous circulation settings, supplying versatility in style and application.
Additionally, MBRs are defined by their compact impact, making them ideal for urban settings with area restraints. Membrane Bioreactor. They also make it possible for the recovery of water for reuse, thus adding to water sustainability campaigns. While MBR modern technology has actually obtained popularity in industrial and community applications, its operational complexities and power needs demand cautious factor to consider throughout implementation. Generally, MBRs go to the center of improving water therapy efficiency and quality, showcasing the potential for cutting-edge services in ecological administration.
Benefits of MBR Technology
The combination of organic treatment with membrane purification offers various benefits for water purification processes. Among the primary advantages of Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) technology is its ability to successfully get rid of both inorganic and organic impurities, bring about premium effluent. The membranes act as a physical barrier, stopping put on hold solids and microorganisms from going through, which enhances the overall security and reliability of treated water.
In addition, MBR systems call for a smaller sized footprint compared to standard therapy methods, allowing for extra effective area use. This compact style is especially advantageous in metropolitan settings where land is limited. MBRs also demonstrate functional flexibility, accommodating varying influent high qualities and circulation prices without considerable performance destruction.
Moreover, the process supplies enhanced nutrient removal capabilities, particularly for nitrogen and phosphorus, which are essential for preventing eutrophication in receiving waters. The reduced sludge production related to MBR modern technology also converts to decrease disposal costs, making it an affordable service in the future - Membrane Bioreactor. In general, the benefits of MBR innovation setting it as a leading choice for sustainable and cutting-edge water purification systems, addressing both ecological and economic worries
Applications in Water Purification
Applications of Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) technology in water filtration are impactful and varied, addressing numerous therapy needs throughout multiple fields. MBRs efficiently integrate organic treatment processes with membrane purification, making them optimal for community wastewater therapy, commercial effluent administration, and also potable water reuse initiatives.
In local settings, MBRs are significantly utilized to improve the high quality of treated wastewater, enabling for conformity with stringent discharge regulations and assisting in the recycling of water for irrigation and non-potable usages. Their compact layout also makes them ideal for urban atmospheres where room is limited.
Industrially, MBR modern technology is used to treat procedure water and wastewater, especially in fields such as food and drink, drugs, and fabrics. By efficiently getting rid of impurities and put on hold solids, MBRs help sectors reduce environmental impacts while recouping important resources from wastewater streams.
Moreover, MBRs are obtaining grip in decentralized water therapy applications, where small systems can be released in remote areas or creating areas. This flexibility enables areas to attain lasting water administration remedies, improving accessibility to tidy water while minimizing reliance on typical therapy techniques.
Study and Success Stories

In one more instance, a fabric production center in Bangladesh took on MBR innovation to resolve its wastewater challenges. The system decreased chemical oxygen need (COD) degrees from 1,200 mg/L to much less than 100 mg/L, thus meeting regulative standards and significantly lessening environmental effect.
The College of Cape Town's MBR installment has actually shown efficient in dealing with greywater for non-potable reuse on school. This project not just preserves drinkable water but additionally works as an educational version for sustainable methods.
Additionally, a seafood processing plant in Norway made use of MBR technology to treat effluents consisting of high levels of natural reference issue, achieving over 90% pollutant elimination. These case researches emphasize MBR technology's convenience and its crucial role in enhancing water high quality throughout varied applications.
Future of Water Therapy Solutions
As international water shortage and air pollution challenges heighten, innovative water treatment remedies are ending up being significantly important to guarantee lasting accessibility to clean water. The future of water therapy depends on the integration of advanced technologies that boost the performance and effectiveness of filtration procedures. Membrane layer bioreactors (MBRs) are at the leading edge of this advancement, combining organic therapy with membrane layer filtration to create more information top quality effluent suitable for various applications.
Arising patterns such as resource healing from wastewater, including nutrients and energy, will additionally change therapy facilities right into environment-friendly centers. Developments in nanotechnology and membrane materials promise improved efficiency and long life of filtration systems.

Conclusion
Finally, membrane layer bioreactors represent a considerable improvement in water filtration technologies, efficiently integrating biological therapy with innovative membrane filtration. The various benefits, consisting of enhanced effluent top quality and decreased spatial requirements, make MBRs specifically ideal for metropolitan applications. Their duty in drinkable water reuse and lasting water management highlights their significance in dealing with worldwide water shortage challenges. Continued research and development will additionally improve the effectiveness and fostering of MBR modern technology, guaranteeing a resistant future for water treatment services.
The introduction of membrane layer bioreactors (MBRs) represents a considerable development in the area of water filtration, combining organic therapy processes with advanced membrane filtration innovations. As global water scarcity magnifies, the duty of MBRs in helping with drinkable water reuse and sustainable water management comes to be increasingly important. They likewise enable the recovery of water for reuse, hence contributing to water sustainability campaigns.As global water Website deficiency and pollution difficulties heighten, cutting-edge water treatment remedies are coming to be increasingly necessary to guarantee sustainable accessibility to tidy water. Their role in potable water reuse and lasting water administration highlights their relevance in addressing global water deficiency challenges.
Report this page